X-Ray Computed Tomography (X-CT) is a non-destructive imaging technique that features high resolution and 3D positioning, making it possible for people to learn about the internal structure and characteristics of cultural relics without causing any damage, thus providing scientists and restorers with much valuable information on the precious and unique cultural relics. Compared with the popular 2D X-ray imaging techniques, X-CT offers 3D imaging results with higher precision and more accurate fault positioning. However, it also requires expensive equipment as well as professionals for operation and maintenance, so there are currently few dedicated pieces of X-CT equipment for cultural relics, which hinders the application of this technique in the industry. The China-Greece Belt and Road Joint Laboratory on Cultural Heritage Conservation Technology not only owns X-CT equipment for cultural relics but also has professional technical personnel to support cultural relic inspection and analysis, and provides strong support for the application and promotion of the X-CT technique in the industry, making a good start for the use of non-destructive testing (NDT) in China and the rest of the world.
Equipment
A X-CT equipment set consists of a 600kV normal-focus X-ray tube, a 225kV micro-focus X-ray tube (focus: 4µm), a flat-panel detector, a linear array detector, and a turntable. It can test cultural relics samples that are up to 60cm in diameter and 100cm in height. It also comes with 3D image processing software, including advanced application modules like the porosity calculation module, so as to meet the varied testing needs for different cultural relic samples and collect data on cultural relic structures more efficiently.
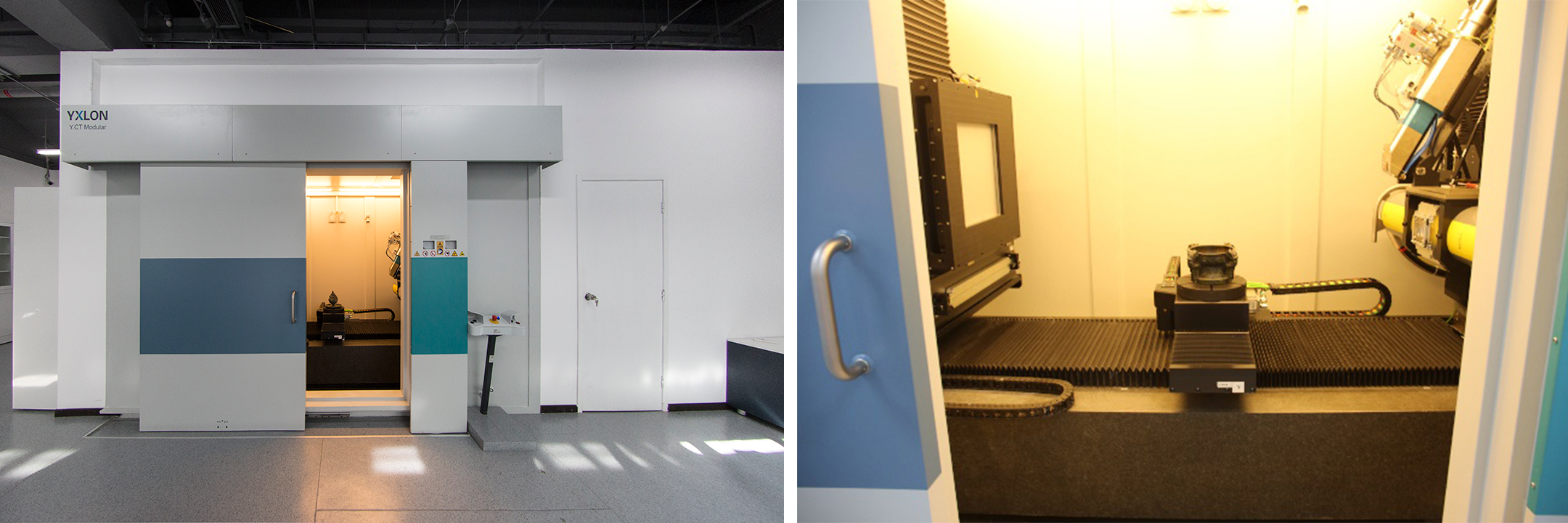 Internal structure of X-ray computed tomography
equipment
Internal structure of X-ray computed tomography
equipment
Applications
Through X-CT, information about the internal structure of cultural relics can be obtained through overall scanning, including but not limited to the location of damages, traces of repair, and the crafts. In addition, due to the high penetration power of X-rays, the equipment is able to test the internal structures of cultural relics made from a variety of materials, such as bronze, lacquer and wood, ceramics, enamel and glass. So far, the technique has generated favorable results on exploring the crafts and traces of repair. Meanwhile, the high-precision data obtained through X-CT can be applied to reverse engineering, so as to create duplicates of cultural relics through 3D printing.
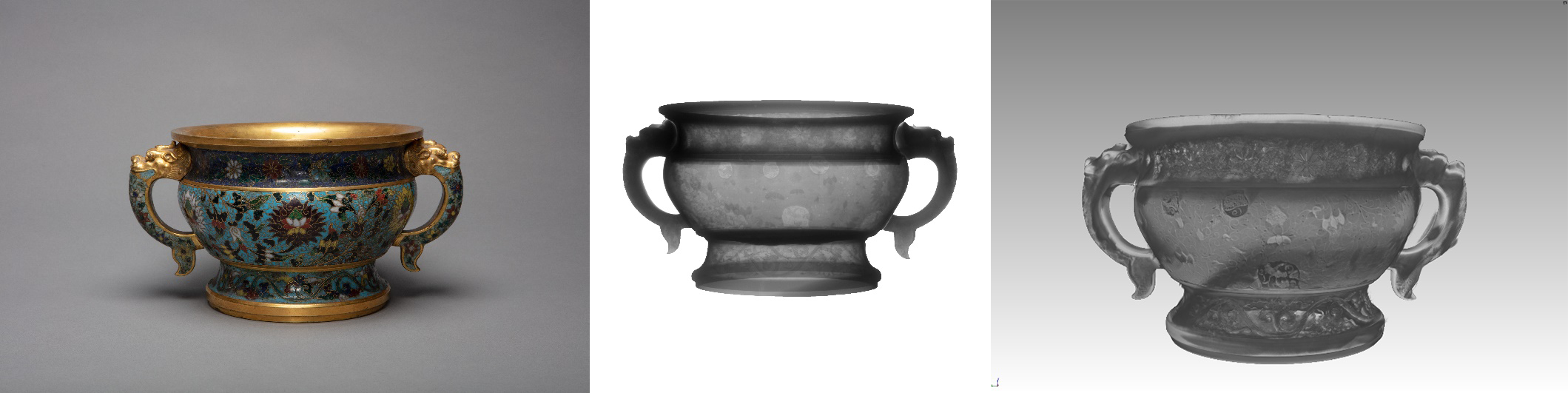 Cloisonné Enamel Censer with
Animal Ear-Shaped Handles, Decorated with Interlocking Sprays of Lotus: 2D
X-ray imaging and 3D X-ray imaging
Cloisonné Enamel Censer with
Animal Ear-Shaped Handles, Decorated with Interlocking Sprays of Lotus: 2D
X-ray imaging and 3D X-ray imaging
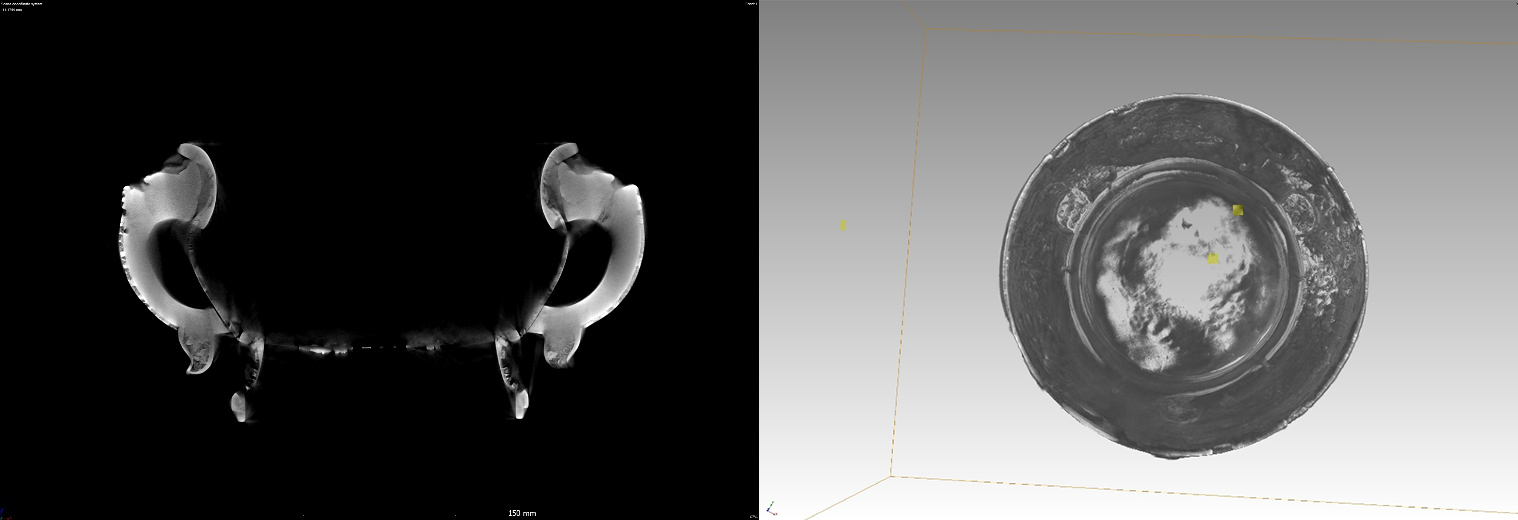
X-CT imaging of the cross-section (Left: Handle embedding structure and enamel thickness. Right: Traces of repair.)